USAF Plane
List
USN
FIGHTERS
LIST OF
PLANES US AIR FORCE WW2
USN WW2
Torpedo Bomber -
Douglas
TBD-1 Devastator
USN WW2
Fighters:
P-38
LIGHTNING
F-82 TWIN
MUSTANG
REPUBLIC
P-47 THUNDERBOLT
NORTH
AMERICAN P-51 MUSTANG
Boeing B-17
Flying Fortress,
Boeing B-29
Superfortress
B-24 D
Liberator
B-25
Mitchell,
Martin B-26
Marauder
B-52
Stratofortress B52
F-14 Tomcat
F-15 Eagle
F15
F-16
Fighting Falcon
F-18 Hornet
F-22 Raptor
F-35 Joint
Strike Fighter U-2 Dragon
Lady SR-71
Blackbird
F-117
Nighthawk F117 F-22 Raptor,
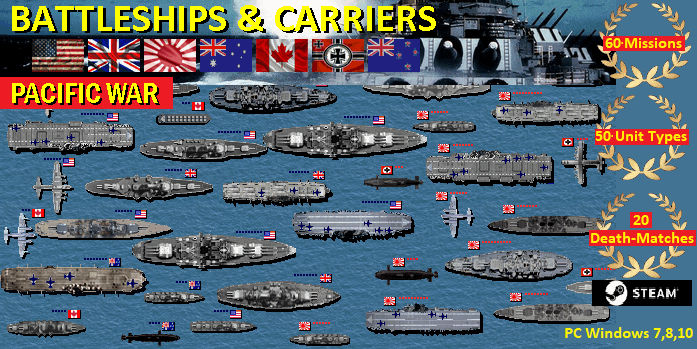
Battleship Game - WW2 Naval
Strategy: the best choice among aircraft carrier games
and battleship games.
Missions and Scenarios:
Pearl Harbor Game
Atlantic Game 1943
Sink Cruisers Game
Midway Game
Iwo Jima Game
US Marines Game
Luftwaffe Game Pacific
Torpedo Game Boats
Bismarck Game Pacific
Destroy RAF Game
Okinawa
Us Navy Submarine Game
Fleet Submarines Game
Kamikaze Game
U Boat Game
Singapore Game
Swordfish Hunt
Patrol Boats
Air Supremacy
Alert
Battleships Game
Java
Defense
Fleet Cruisers Game
Atlantic Island
Coral Sea Game
Iron Sea
Mykonos
Imperial Ocean
Long Convoy
Skagerrak
Target Los Angeles
West Pacific Game
Pacific War Game
Leyte Transport
Emperor Hirohito
Normandy Game
South Pacific Game
Destroy USAF Game
Submarine Games
US Navy Game
Free Hunt Doenitz Game
Free Hunt Spruance Game
Free Hunt Halsey Game
Imperial Navy I
Royal Navy Game
Free Hunt Pearl Harbor Games
Midway II
Kriegsmarine I
Brisbane Convoy
Clear West Coast
Fall Of Australia
Battle For Leyte
Conquer Of Japan
HMAS Perth
Road To Okinawa
Orange Ports
Emperor Defense
Prince Of Wales
San Bernardino
Pacific Race
Heavy Duty
Tokio Express
Operation Sidney
Bomber Operation
Conquer Of Italy
Heavy Cruiser Game
Frigate Hunt
Santa Cruz
Lamansh Game
Azores Transport
Norway Convoy
Invasion
Grossadmiral
Norway Ports
Drang Nach Ost
Convoy Pk30
Ciano Defense
Sir John Tovey
Free Hunt Andrews
Germans On Pacific
Silent Hunt
Antigua
Return To Midway
Kriegsmarine Game II
Royal Air Force Game
F. Hunt Lancaster
Jamamoto Game
Free Hunt USN
Free Hunt Japan
Free Hunt RAAF
Free Hunt U Boat Game
Free Hunt Aircraft Carriers Game
Free Hunt Hawaii
Free Hunt Yamato Game
Free Hunt Iwo Jima Game
Free Hunt Pacific Game
Free Hunt Torpedos
Free Hunt Convoy
Free Hunt Germany
Free Hunt Germany II
Free Hunt Italy
Free Hunt Malaya
Free Hunt Subs Game
Free Hunt B-26 Game
Free Hunt USN 1944
Devil Island
Dragoon Carriers
|
B24 Liberator
 |
 |
| B24 |
B-24 |
B-24: often compared
to the better known B-17 Flying Fortress, the B-24 was a
more modern design with a higher top speed and greater
range yet it had a similar bomb load and defensive
armament. Nevertheless, popular opinion among aircrews
and general staff tended to favor the B-17's rugged
qualities above all other considerations.
The B-24 was notorious among American air crews for its
tendency to catch fire. The placement of the B-24's fuel
tanks throughout the upper fuselage and its lightweight
construction, designed both to increase range and
optimize assembly line production, made the aircraft
vulnerable to battle damage
The B24 ( B-24 )was employed in operations in every
combat theater during the war. Because of B24 s great
range, it was particularly suited for such missions as
the famous raid from North Africa against the oil
industry at Ploesti, Rumania, Aug. 1, 1943. This feature
also made the airplane suitable for long, over-water
missions in the Pacific Theater. More than 18,000
Liberators were produced.
B24
Specifications
Span:
110 feet
B24 Length: 66 feet, 4 inches
Height: 17 feet, 11 inches
B-24 Weight: 56,000 pounds loaded
Armament: Ten .50-cal. machine guns and 8,000 pounds of
bombs
B24 Engines: Four Pratt &;Whitney R 1830s of 1,200
horsepower each
Cost: $336,000
B24
Performance
B-24
Maximum speed: 303 mph.
B24 Cruising speed: 175 mph.
B-24 Range: 3,200 mph.
B24 Service Ceiling: 28,000 feet
B-24
Variants and conversions
X B-24 (Consolidated Model 32)
Designed in 1938 as an improvement on the B-17 Flying
Fortress, at the request of the Army Air Corps. It had a
wing specially designed for a high aspect ratio, tricycle
landing gear, and twin vertical stabilizers. The XB-24
was ordered in 1939 March, and first flew on 29 December
1939. (Total: one)
Y B-24 / LB-30A Preproduction prototypes
Six examples were sent to Great Britain under lend-lease,
under the designation LB-30A.
B-24
Service test version of the XB-24, ordered on 27 April
1939, less than 30 days after the XB-24 was ordered,
before the XB-24 design was complete. A number of minor
modifications were made: elimination of leading edge
slots, addition of de-icing boots. (Total: seven; only
one used for actual testing)
B-24 ex-"Diamond Lil" from the Commemorative
Air Force collection. Airframe returned to B-24 A
configuration in 2007 and renamed "Ol 927".
B24 A/LB-30B
Ordered in 1939, the B-24A was the first production
model. Due to the need for heavy bombers, the B-24A was
ordered before any version of the B-24 flew. The main
improvement over the XB-24 was improved aerodynamics,
which led to better performance. Some sent to Great
Britain under Lend Lease as LB-30B. (Total: 38,20
LB-30Bs, nine B-24Cs)
| CIA / KGB intelligence game. Run your own operation game.
Travel around the world and set up espionage
game, trade with state secrets, weapon systems,
spy codes, WMD, hire secretaries, agents, lawyers
and soldiers, establish secret agent stations,
cells and bases and search for criminals and
politicians. Involve in agent game. Game contains
more than 40 missions including Nuclear Game,
Cold War Game, Secret Agent, CIA Games, USAF,
Prime Minister, RAF, Bin Laden, Sadam, KGB,
Operations Iran… |
|
X B-24 B
When the XB-24 failed to reach its projected top speed,
the Pratt & Whitney R-1830-33 radials rated at 1,000
hp (746 kW) it carried were replaced with R-1830-41
turbo-supercharged radials rated at 1,200 hp (895 kW),
increasing its top speed by 37 mph (59 km/h). The
addition of the turbo-superchargers made the engine
cowlings elliptical. The XB-24B version also lacked the
engine slots of the original. (Total: one converted
XB-24)
B-24C
Conversion of the B-24A using turbo-supercharged
R-1830-41 engines. To hold the supercharger and the
intercooler intake, the cowlings were made elliptical and
the new items added on the sides. The tail gunner
position was improved by adding an Emerson A-6 power
turret with twin .50-caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns; a
Martin power turret was added to the forward fuselage.
(Total: nine converted B-24As)
B-24 D
First model produced on a large scale; ordered from 1940
to 1942, as a B-24C with better engines (R-1830-43
supercharged engines). During the production run, the
tunnel gun in the belly was replaced by a remote-sited
Bendix belly turret; this was later replaced by a Sperry
ball turret. In late B-24Ds, 'cheek' guns were added.
(Total: 2696, 2381 Consolidated, San Diego; 305
Consolidated, Fort Worth, ten Douglas, Tulsa, Oklahoma)
B-24 E
A slight alteration of the B-24D built by Ford, using
R-1830-65 engines. Unlike the B-24D, the B-24E retained
the tunnel gun in the belly. The USAAF used the B-24E's
primary as training aircraft since this model was not
current in armaments and other technology as the aircraft
being produced by Consolidated / San Diego (CO). Ford
also built sub-assemblies for Douglas; these
sub-assemblies were identical to Ford-built B-24Es,
except that they used the same engines as the B-24D
(R-1830-43 radials). These sub-assemblies were called PK
ships and were shipped by truck from Willow Run to the
final assembly in Tulsa, Oklahoma. (Total: 801)
X B-24 F
A prototype made to test thermal de-icers, instead of the
standard inflatable rubber "boots." (Total: one
converted B-24D)
B-24 G
Sperry ball turret, three .50 caliber- (12.7 mm) machine
guns in nose. All B-24Gs were built by North American
Aviation, which was contracted in 1942. (Total: 25)
B-24G-1
Modified Emerson A-6 tail turret in nose instead of two-
three .50 caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns in earlier
models. The B-24G-1 was based on the design of the B-24H
(Total: 405)
B24 H
Because of obvious vulnerability of the B-24 to head-on
attack, the B-24 H design made by Ford used a nose
turret, generally a modified Emerson A-6 tail turret. The
entire aircraft was redesigned to better fit the turret;
50 airframe changes were made, including a redesigned
bombardier compartment. The tail turret was given larger
windows for better visibility, the top turret a higher
bubble, and the waist gunner positions were offset, to
reduce their interference during battle. (Total: 3100)
Consolidated B-24J-55-CO Liberator, Serial number
42-99949 belonged to 93rd BG, 328th BS; lost 21 September
1944 over Belgium.
Consolidated B-24J-55-CO Liberator, Serial number
42-99949 belonged to 93rd BG, 328th BS; lost 21 September
1944 over Belgium.
B-24 J
The B-24J was very similar to the B-24H, although the
defensive improvements made in the B-24H were not
incorporated in the B-24J. The B-24J featured an improved
autopilot (type C-1) and a bombsight of the M-1 series.
B-24H sub-assemblies made by Ford and constructed by
other companies and any model with a C-1 or M-1 retrofit,
were all designated B-24Js. (Total: 6678)
X B24 K
An experimental aircraft, made by Ford by splicing a B-23
Dragon tail empennage onto a B-24D airframe. The aircraft
was more stable and had better handling than other
models, but changing the B-24 design was too expensive to
do at the time. However, the XB-24K was the ancestor of
the Navy's PB4Y-1. (Total: one converted B-24D)
B-24L
Because of the immense weight of the B-24J, the Army
pushed for a lighter version. In the B-24L, the ball
turret was replaced by a floor ring mount with two .50
caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns, and the A-6B tail turret
by an M-6A. In later aircraft, no tail armament was
installed, and when it arrived at its airfield, either an
A-6B, an M-6A, or a dual-mount manual .50-caliber (12.7
mm) gun was field-installed. (Total: 1667)
B24 M
An enhancement of the B-24L with further weight-saving
devices. The B-24M used a more lightweight version of the
A-6B tail turret; the waist gunner positions were left
open. For better visibility, the windshield was replaced
by a "knife-edge" dual pane versions. The B-24M
became the last production model of the B-24; a number of
the B-24s built flew only the course between the factory
and the scrap heap. (Total: 2593)
X B24 N
A redesign of the B-24J, made to accommodate a single
tail. It also featured improved nose and tail turrets.
While 5168 B-24Ns were ordered, World War II ended and
there was no longer any need for them. (Total: one)
Y B-24 N
Pre-production service test version of the
XB-24N. (Total: seven)
X B-24 P
A modified B-24D, made by Sperry Gyroscope Company to
test airborne fire control systems. (Total: one converted
B-24D)
X B-24 Q
A General Electric conversion of the B-24L,
using radar-controlled tail turrets. (Total: one
converted B-24L).
XB-41
Because there were no fighters capable of
escorting bomber formations on deep strike missions early
in World War II, the Army authorized tests for heavily
armed bombers to act as escorts for bombing missions. It
was completed in 1942. The results of 1943 testing were
very negative and the project was quickly cancelled.
Performance changed drastically with the addition of more
turrets. The escorts were also unable to keep up with
bomber formations once the bombs had been dropped.
The XB-41 had 14, .50-caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns,
through the addition of a Bendix chin turret and a dorsal
Martin power turret on the mid-fuselage. (Total: one
converted B-24D)
AT-22 or TB-24
R B-24 L
Developed for training B-29 gunners on an
identical remote gun system installed on a B-24L.
T B-24 L
As with the RB-24L, but with additional radar
equipment.
C-87 Liberator Express
Passenger transports with accommodation for 20
passengers.
XF-7
Photographic reconnaissance variant developed from the
B-24D.
F-7
Photographic reconnaissance variant developed from the
B-24H; -FO block.
F-7A
Photographic reconnaissance variant developed from the
B-24J; three cameras in the nose and three in the bomb
bay.
F-7B
Photographic reconnaissance variant developed from the
B-24J; six cameras in the bomb bay.
U.S. Navy Nomenclature and Subvariants
PB4Y-1
B-24 D with different nose turret for U.S. Navy.
Designation later applied to all G, J, L and M models
received by the U.S. Navy.
PB4Y-1P
Photographic reconnaissance variant developed from the
PB4Y-1.
PB4Y-2 Privateer
RY-1
U.S. Navy designation for the C-87A.
RY-2
U.S. Navy designation for the C-87.
RY-3
Transport variant of the PB4Y-2.
British Nomenclature and subvariants
Liberator B Mk I
B-24A (Total: 20), used in British Coastal
Patrol and Defense Squadrons.
Liberator B Mk II
The first combat ready B24. The modifications included a
three foot nose extension as well as a deeper aft
fuselage and wider tailplane – there was no direct
B-24 equivalent but similar to the B-24 C - built to meet
British specifications with British equipment and
armament. A small series of B Mk IIs were reconstructed
as unarmed transports, designated the LB-30 with the
USAAF. (Total production: 165)
Liberator B Mk III
B-24 D variant with single .303 Browning machine gun in
the nose, two in each beam position, and four in a
Boulton Paul tail turret similar to that on the
Lancaster, as well as, other British equipment. The
Martin dorsal turret was retained. (Total: 156)
Liberator B Mk IIIA
Lend-Lease B-24Ds with American equipment and
weapons.
Liberator B Mk IV
Reserved for the B-24E, but there is no record of the RAF
actually receiving any.
Liberator B Mk V
B-24D modified for extra fuel capacity at the cost or
armor, with the same armament fit as the Liberator Mk
III.
Liberator B Mk VI
B-24Hs in RAF service fitted with Boulton Paul tail
turrets, but retaining the rest of their armament.
Liberator B Mk VIII
RAF designation for B-24Js.
Liberator GR Mk V
B24 D modified by RAF Coastal Command for the
anti-submarine role with search radar and Leigh Light.
Some were fitted with eight zero-length rocket launchers,
four on each wing.
Liberator GR Mk VI
B24 G/H/J type used as a long-range general
reconnaissance aircraft by RAF Coastal Command.
Liberator GR Mk VIII
B-24J modified by RAF Coastal Command for the
anti-submarine role.
Liberator C Mk VI
Liberator B Mk VIII converted for use as a transport.
Liberator C Mk VII
British designation for C-87.
Liberator C Mk VIII
Liberator G Mk VIII converted for use as a transport.
Liberator C Mk IX
RAF designation for the RY-3/C-87C
B24 PRODUCTION
Continued development work by Consolidated produced a
handful of transitional B-24Cs with turbocharged instead
of supercharged engines. The turbocharged engines led to
the flattened oval nacelles that distinguished all
subsequent Liberator models.
The first mass-produced model was the B-24D (Liberator
III in British service), entering service in early 1943.
It had turbocharged engines and increased fuel capacity.
Three more 0.50 caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns brought
the defensive armament up to 10 machine guns. At 59,524
lb (27,000 kg) maximum takeoff weight, it was one of the
heaviest aircraft in the world; comparable with the
British "heavies" the Stirling, Lancaster and
Halifax.
B-24s under construction at Ford Motor's Willow Run plant
Production of B-24s increased at an astonishing rate
throughout 1942 and 1943. Consolidated Aircraft tripled
the size of its plant in San Diego and built a large new
plant outside Fort Worth, Texas. More B-24s were built by
Douglas Aircraft in Tulsa, Oklahoma. North American
Aviation built a plant in Dallas, Texas, which produced
B-24Gs and B-24Js.[citation needed] None of these were
minor operations, but they were dwarfed by the vast new
purpose-built factory constructed by the Ford Motor
Company at Willow Run near Detroit, Michigan. Ford broke
ground on Willow Run in the spring of 1941, with the
first plane coming off the line in October 1942. It had
the largest assembly line in the world (3,500,000
ft?/330,000 m?). At its peak, the Willow Run plant
produced 650 B-24s per month in 1944. By 1945, Ford made
70% of all B-24s in two nine-hour shifts. Pilots and
crews slept on 1,300 cots at Willow Run waiting for their
B-24s to roll off the assembly line. At Willow Run, Ford
produced half of 18,000 total B-24s.
Each of the B-24 factories was identified with a
production code: Consolidated/San Diego, CO;
Consolidated/Fort Worth, CF; Ford/Willow Run, FO; North
American, NT; and Douglas/Tulsa, DT.
In 1943, the model of Liberator considered by many the
"definitive" version was introduced. The B24 H
was 10 in (25 cm) longer, had a powered gun turret in the
upper nose to reduce vulnerability to head-on attack and
was fitted with an improved bomb sight, autopilot, and
fuel transfer system. Consolidated, Douglas and Ford all
manufactured the B-24H, while North American made the
slightly different B-24G. All five plants switched over
to the almost identical B-24J in August 1943. The later
B24 L and B24 M were lighter-weight versions and differed
mainly in defensive armament.[citation needed]
WASP pilots (left to right) Eloise Huffines Bailey,
Millie Davidson Dalrymple, Elizabeth McKethan Magid and
Clara Jo Marsh Stember, with a B-24 in the background
As the war progressed, the complexity of servicing the
Liberator continued to increase. The B24 variants made by
each company differed slightly, so repair depots had to
stock many different parts to support various models.
Fortunately, this problem was eased in the summer of
1944, when North American, Douglas, and Consolidated
Aircraft at Fort Worth stopped making B-24s, leaving only
the Consolidated plant in San Diego and the Ford plant in
Willow Run.[citation needed]
In all, 18,482 B-24s were built by September 1945. Twelve
thousand saw service with the USAAF. The U.S. Navy
operated about 1,000 PB4Y-1s, and almost 800 PB4Y-2
Privateers which were derived from the B-24. The Royal
Air Force flew about 2,100 B-24s in 46 bomber groups and
41 squadrons; the Royal Canadian Air Force 1,200 B-24Js;
and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) 287 B-24Js,
B-24Ls, and B-24Ms. Liberators were the only heavy bomber
flown by the RAAF in the Pacific. Two squadrons of the
South African Air Force based in Italy flew B24s.
(credits: US Air Force
History Support Office)
|
| The
B-24 was more difficult to fly as well, with
heavy control forces and poor formation flying
characteristics. The B-24 nevertheless provided
excellent service in a variety of roles thanks to
its large payload and long range. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Turn-based
trade strategy game.
Build your own world empire as an arms
dealer.
Trade with weapons, hire spies, agents,
secretaries, bodyguards and lawyers, and
establish bases and spy cells worldwide.
Trading cards game combat system
included.
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Guns
Girls Lawyers Spies is a trade
management game. You'll build
your multinational spy company, destroy
competition, hire employees, spies, and
businessman, establish spy cells, bases
and objects.
There is a more than 40 missions with
different game objectives. |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Tycoon Strategy
Game - build your own world business empire as an
arms dealer tycoon. Travel around the world,
trade with more than 400 weapon systems, hire
secretaries, bodyguards, lawyers, fighters and
tanks, establish companies and search for
criminals and hostages. |
|
| |
|