USAF Plane
List
USN
FIGHTERS
A-10
Thunderbolt II
F-5 Freedom
Fighter
F-20
Tigershark
F-4 Phantom
II
F-86 Sabre,
A-4 Skyhawk,
A-6 Grumann
Intruder
F-14 Tomcat
F-15 Eagle
F15,
F-16
Fighting Falcon
F-18 Hornet
F-22 Raptor
F-35 Joint
Strike Fighter
U-2 Dragon
Lady
SR-71
Blackbird
F-22 Raptor,
F-35 Joint
Strike Fighter JSF
B-52
Stratofortress B52
F-111
B-2 Spirit
P-3C Orion
S-3B Viking
CH-46 Sea
Knight,
CH-53 Sea
Stallion
H-3 Sea
King
MH-53 Sea
Dragon
SH-60
Seahawk
HH/UH-1N
Iroquois
AH-1 Cobra
UH-60 Black
Hawk,
HH-60 Pave
Hawk Helicopter
AH-64
Apache AH64
RQ-1
Predator
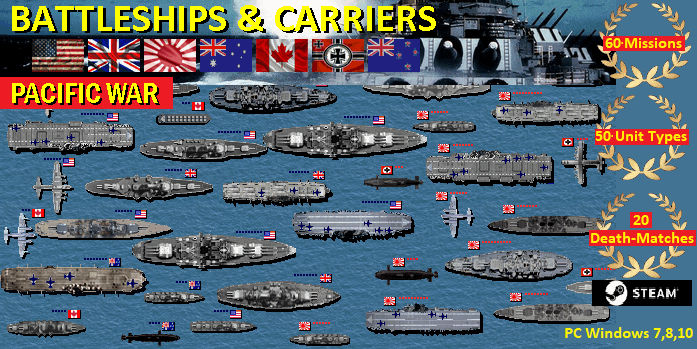
Battleship Game - WW2 Naval
Strategy: the best choice among aircraft carrier games and submarine and battleship games.
|
B-1 Lancer
The Boeing B-1B Lancer is a
long-range heavy bomber in service with the USAF since
1986. Together with the B-52 Stratofortress it is the backbone of the United States's
long-range bomber force.
The B-1A model never went into production. The USAF
acquired four prototype flight test models in the 1970s,
but the program was canceled in 1977. Flight test of the
four B-1A models continued through 1981.
The B-1B is the improved variant initiated by the Reagan
administration in 1981. The first production model flew
in October 1984, and the first B-1B was delivered to
Dyess Air Force Base, Texas, in June 1985, with initial
operational capability on October 1, 1986. The final B-1B
was delivered May 2, 1988. A total of 90 front-line
aircraft were produced at a cost of over $200 million
each.
B-1 Technology
The B-1B has a blended wing and
body configuration, along with variable-geometry design
and turbofan enginess, to improve range and speed with
enhanced survivability. Forward wing settings are used
for takeoff, landings and high-altitude maximum cruise.
Aft wing settings are used in high subsonic and
supersonic flight, enhancing the B-1B's maneuverability.
The B-1B's offensive avionics include the forward-looking
offensive radar set employing synthetic aperture radar,
ground moving target indicator and terrain-following
radar modes, an extremely accurate Global Positioning
System/Inertial Navigation System, the avionics control
unit complex, a Doppler radar, and a radar altimeter.
These features enable aircrews to globally navigate,
accurately refine aircraft position without the need for
ground-based navigation aids, update mission information
and target coordinates in-flight, and perform precision
bombing.
The B-1B's electronic jamming equipment, infrared
countermeasures, radar location and warning systems
combine with its low-radar cross-section to aid the
aircrat's survival in hostile airspace. The current
defensive avionics system consist of the ALQ-161A radio
frequency surveillance and electronic countermeasures
system, the tail warning function, and the expendable
countermeasures system, and is supplemented by the ALE-50
Towed Decoy System.
The defensive avionics system is a comprehensive
electronic countermeasures package that detects enemy
threats and applies the appropriate countermeasures, such
as electronic jamming or dispensing expendable chaff and
flares to protect against radar-homing and heat-seeking
missiles. The TDS complements the system by providing
greater protection against RF threats. Low-radar
cross-section is provided by the combination of aircraft
structure and radar-absorption materials that reduce the
aircraft's radar signature to approximately 1 percent
that of the B-52. Similar
to the offensive avionics, the defensive suite has a
reprogrammable design that allows in-flight changes to be
made to counter new or changing threats.
The B1-B has been upgrade since production through the
Conventional Mission Upgrade Program. This has improved
the precision and standoff weapons and the electronic
countermeasures suite. The upgrade program includes GPS
receivers, a weapons interface which enables the use of
the joint direct attack munition and other weapons,
secure radios, and improved computers to support new
precision and near-precision weapons such as the
wind-corrected munitions dispenser, the joint standoff
weapon, the joint air-to-surface standoff missile.
These improvements help lay the foundation for future
precision miniature munitions, such as Small Diameter
Bomb. These and other improvements such as the
replacement of the current ALQ-161 with the ALQ-214
Integrated Defensive Electronic Counter-Measures, are
intended to ensure that the B-1 will be viable up to and
beyond 2010.
The B-1B holds several world records for speed, payload
and distance. The National Aeronautic Association
recognized the B-1B for completing one of the 10 most
memorable record flights for 1994.
The B-1B was first used in combat in support of
operations against Iraq during Operation Desert Fox in
December 1998. B-1s have been subsequently used in
Operation Allied Force.
| CIA / KGB Operation
Game.
Run your own intelligence game. Travel around the
world and set up espionage game, trade with state
secrets, weapon systems, spy codes, WMD, hire
secretaries, agents, lawyers and soldiers,
establish secret agent stations, cells and bases
and search for criminals and politicians. Involve
in agent game. Game contains more than 40
missions including Nuclear Game, Cold War Game,
Secret Agent, CIA Games, USAF, Prime Minister,
RAF, Bin Laden, Sadam, KGB, Operations Iran… |
|
B-1 General Characteristics
| Primary Function: |
Long-range, multi-role,
heavy bomber |
| Builder: |
Boeing, North America
(formerly Rockwell International, North American
Aircraft) |
| Operations Air Frame and
Integration: |
Offensive avionics, Boeing
Military Airplane; defensive avionics, AIL
Division |
| Power plant: |
Four General Electric
F-101-GE-102 turbofan engine with afterburner |
| Thrust: |
30,000-plus pounds with
afterburner, per engine |
| Length: |
146 feet (44.5 meters) |
| Wingspan: |
137 feet (41.8 meters)
extended forward, 79 feet (24.1 meters) swept aft |
| Height: |
34 feet (10.4 meters) |
| Weight: |
Empty, approximately
190,000 pounds (86,183 kilograms) |
| Maximum Takeoff
Weight: |
477,000 pounds (216,634
kilograms) |
| Speed: |
900-plus mph (Mach 1.2 at
sea level) |
| Range: |
Intercontinental,
unrefueled |
| Ceiling: |
More than 30,000 feet
(9,144 meters) |
| Crew: |
Four (aircraft commander,
copilot, offensive systems officer and defensive
systems officer) |
| Armament: |
Three internal weapons bays
can accommodate up to 84 Mk-82 general purpose bombs
or Mk-62 naval mines, 30 CBU-87/89 cluster
munitions or CBU-97 Sensor Fused Weapons and up
to 24 GBU-31 JDAM GPS guided bombs or Mk-84
general purpose bombs |
| Date
Deployed: |
June 1985 |
| Unit
Cost: |
$200-plus million
per aircraft |
| Inventory: |
Active force, 72;
ANG, 18; Reserve, 0 |
B1 Features
The B-1B's blended wing/body
configuration, variable-geometry wings and turbofan
afterburning engines, combine to provide long range,
maneuverability and high speed while enhancing
survivability. Forward wing settings are used for
takeoff, landings, air refueling and in some
high-altitude weapons employment scenarios. Aft wing
sweep settings - the main combat configuration -- are
typically used during high subsonic and supersonic
flight, enhancing the B-1B's maneuverability in the low-
and high-altitude regimes. The B-1B's speed and superior
handling characteristics allow it to seamlessly integrate
in mixed force packages. These capabilities, when
combined with its substantial payload, excellent radar
targeting system, long loiter time and survivability,
make the B-1B a key element of any joint/composite strike
force.
The B-1 is a highly versatile, multi-mission weapon
system. The B-1B's synthetic aperture radar is capable of
tracking, targeting and engaging moving vehicles as well
as self-targeting and terrain-following modes. In
addition, an extremely accurate Global Positioning
System-aided Inertial Navigation System enables aircrews
to navigate without the aid of ground-based navigation
aids as well as engage targets with a high level of
precision. The Combat Track II radios provide a secure
beyond line of sight reach back connectivity until
Link-16 is integrated on the aircraft. In a time
sensitive targeting environment, the aircrew can use
targeting data from the Combined Air Operations Center
over Combat Track II, then to strike emerging targets
rapidly and efficiently. This capability was effectively
demonstrated during operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi
Freedom.
The B-1B's onboard self-protection electronic jamming
equipment, radar warning receiver (ALQ-161) and
expendable countermeasures (chaff and flare) system and a
towed decoy system (ALE-50) complements its low-radar
cross-section to form an integrated, robust defense
system that supports penetration of hostile airspace. The
ALQ-161 electronic countermeasures system detects and
identifies the full spectrum of adversary threat emitters
then applies the appropriate jamming technique either
automatically or through operator inputs.
Current modifications build on this foundation. Radar
sustainability and capability upgrades will provide a
more reliable system and may be upgraded in the future to
include an ultra high-resolution capability and automatic
target recognition. The addition of a fully integrated
data link, or FIDL, will add Link-16 communications
capability. FIDL combined with associated cockpit
upgrades will provide the crew with a much more flexible,
integrated cockpit, and will allow the B-1 to operate in
the fast-paced integrated battlefield of the future.
Several obsolete and hard to maintain electronic systems
are also being replaced to improve aircraft reliability.
B-1 Operational history
The second B-1B, "The Star of
Abilene", was the first B-1B delivered to the USAF
Strategic Air Command (SAC) in June 1985. Initial
operational capability was reached on 1 October 1986 and
the B-1B was placed on nuclear alert status. The B-1
received the official name "Lancer" on 15 March
1990. However, the bomber has been commonly called the
"Bone"; a nickname that appears to stem from an
early newspaper article on the aircraft wherein its name
was phonetically spelled out as "B-ONE" with
the hyphen inadvertently omitted.
A dismantled decommissioned B-1 being transported by
flatbed truck
In late 1990 engine fires in two Lancers caused the
grounding of the fleet. The cause was traced back to
problems in the first-stage fan, the aircraft were placed
on "limited alert"; in other words, they were
grounded unless a nuclear war broke out. Following
inspections and repairs they were returned to duty
beginning on 6 February 1991. Due to the engine problems,
the B-1B was effectively sidelined in the First Gulf War.
Originally designed strictly for nuclear war, the B-1's
development as an effective conventional bomber was
delayed until the 1990s. The collapse of the Soviet Union
had brought the B-1's nuclear role into question, leading
to President George H. W. Bush ordering a $3 billion
conventional refit. By 1991, the B-1 had a fledgling
conventional capability, forty of them able to drop the
500 pounds (230 kg) Mk-82 General Purpose (GP) bomb,
although mostly from low altitude. Despite being cleared
for this role, the problems with the engines precluded
their use in Operation Desert Storm. B-1s were primarily
reserved for strategic nuclear strike missions at this
time, providing the role of airborne nuclear deterrent
against the Soviet Union. The B-52 was more suited to the
role of conventional warfare and it was used by coalition
forces instead.
After the inactivation of Strategic Air Command (SAC) and
the establishment of the Air Combat Command (ACC) in
1992, the B-1 developed a greater conventional weapons
capability. Part of this development was the start-up of
the U.S. Air Force Weapons School B-1 Division. In 1994,
two additional B-1 bomb wings were also created in the
Air National Guard, with former fighter wings in the
Kansas Air National Guard and the Georgia Air National
Guard converting to the aircraft. By the mid-1990s, the
B-1 could employ GP weapons as well as various CBUs. By
the end of the 1990s, with the advent of the "Block
D" upgrade, the B1 boasted a full array of guided
and unguided munitions. The B-1B no longer carries
nuclear weapons; its nuclear capability was disabled by
1995 with the removal of nuclear arming and fuzing
hardware
B1 Variants
B-1A
The B-1A was the original B-1 design with variable engine
intakes and Mach 2.2 top speed. Four prototypes were
built; no production units were manufactured.
B-1B
The B-1B is a revised B-1 design with reduced radar
signature and a top speed of Mach 1.25. It was otherwise
optimized for low-level penetration. A total of 100 B-1Bs
were produced.
B-1R
The B-1R is a proposed upgrade of existing B-1B
aircraft.The B1-R would be fitted with advanced radars,
air-to-air missiles, and new Pratt & Whitney F119
engines. This variant would have a top speed of Mach 2.2,
but with 20% less range.
Existing external hardpoints would be modified to allow
multiple conventional weapons to be carried, increasing
overall loadout. For air-to-air defense, an Active
Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar would be added
and some existing hardpoints modified to carry air-to-air
missiles. If needed the B1-R could escape from
unfavorable air-to-air encounters with its Mach 2+ speed.
Few aircraft are currently capable of sustained speeds
over Mach 2.
|
337th Bomb Squadron 1985-93
338th Combat Crew Training Squadron 1986-93
4018th Combat Crew Training Squadron 1985-86
319th Bomb Wing - Grand Forks AFB, North Dakota 1987-94
46th Bomb Squadron
366th Wing - Mountain Home AFB, Idaho 1997-2002
34th Bomb Squadron
384th Bomb Wing - McConnell AFB, Kansas 1987-94
28th Bomb Squadron
Air National Guard
116th Bomb Wing - Robins AFB. Georgia 1996-2002
128th Bomb Squadron
184th Bomb Wing - McConnell AFB, Kansas 1994-2002
127th Bomb Squadron
USAF Flight Test Center - Edwards AFB, California
412th Operations Group 1989-92
410th Flight Test Squadron
412th Test Wing 1992–present
419th Flight Test Squadron
6510th Test Wing 1974-89
6519th Flight Test Squadron
| |
 |
 |
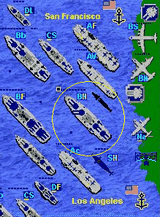
| Turn-based WW2
naval game, extension to the classic
Submarine game (Battleship game) where
ships/planes/subs can move. Contains plenty of
game missions, game campaigns and 40 ship,
submarine, airplane ana port artillery types,
with combat maps up to 96X96 large. |
| |
| |
| |
|
| Tycoon Strategy
Game - build your own world business empire as an
arms dealer tycoon. Travel around the world,
trade with more than 400 weapon systems, hire
secretaries, bodyguards, lawyers, fighters and
tanks, establish companies and search for
criminals and hostages. |
| |
|